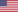
Vehicle Access Control Systems are security systems that restrict or allow access to vehicles in specific areas, such as parking lots, gated communities, or government facilities. These systems use a variety of technologies, including RFID tags, license plate recognition, key cards, and biometric identification, to control access to the area.
What Are Vehicle Access Control Systems
The purpose of Vehicle Access Control Systems is to ensure that only authorized vehicles are allowed entry into a specific area. This helps to prevent theft, vandalism, and unauthorized access. Additionally, these systems can be used to monitor and control the flow of vehicles, such as managing the number of vehicles entering and exiting a parking lot.
Free Online Estimate of Vehicle Access Control Systems
There are several types of vehicle access control systems available, each with its own set of features and benefits. Some examples include:
Barrier systems: These are physical barriers, such as gates or bollards, that prevent vehicles from entering a restricted area.
RFID systems: These use radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to detect and identify authorized vehicles.
License plate recognition systems: These use cameras to capture license plate numbers and compare them to a list of authorized vehicles.
Key card systems: These use key cards or access cards to allow entry to authorized vehicles.
Biometric systems: These use biometric data, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to identify authorized drivers and allow entry to the restricted area.
Overall, Vehicle Access Control Systems provide an effective way to manage and control access to restricted areas, helping to improve security and safety for both people and property.
Vehicle access control systems and software developed by FRESH USA have the best solutions. For more information, follow the link about parking systems.
We provide Lifetime Software License. No Subscriptions, No Monthly Fees!
Parking Management Software Free Download
Vehicle Access Control And RFID Technology
Vehicle Access Control Systems with RFID UHF (Ultra-High Frequency) technology are a type of access control system that uses radio waves to identify and track vehicles. UHF RFID technology operates in the frequency range of 860 MHz to 960 MHz, allowing for longer read range and faster data transfer rates compared to other RFID technologies.
You can order a reliable and advanced vehicle access control systems from Fresh USA.
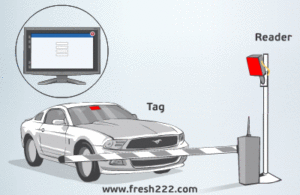
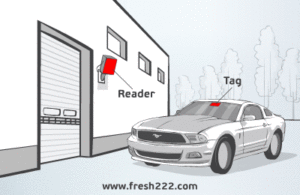
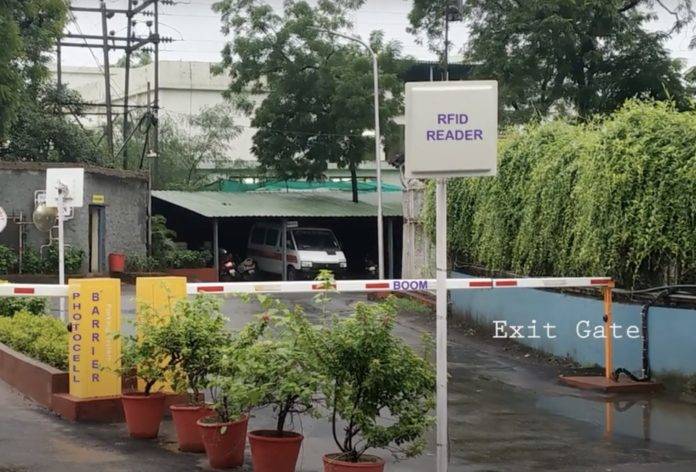
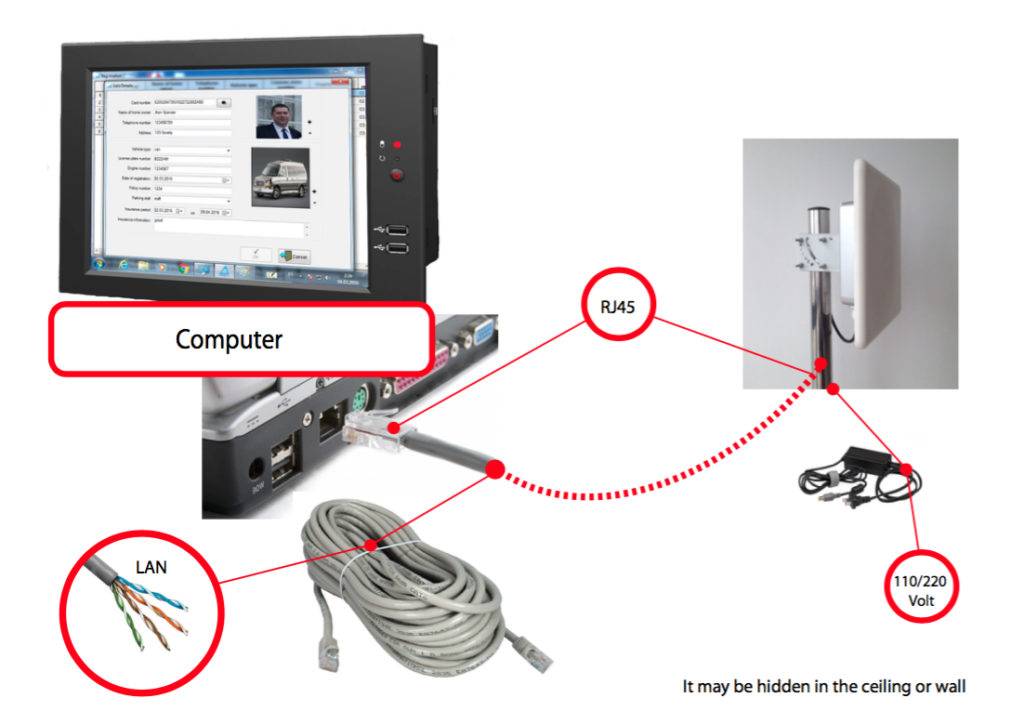
In a typical RFID UHF-based Vehicle Access Control System, each vehicle is equipped with an RFID tag*, which contains a unique identification number. The reader antenna is installed at the entrance or exit of the restricted area and emits a radio frequency signal to detect the RFID tag. When the RFID tag is within range of the reader antenna, it sends back the unique identification number to the reader.
* Parking access control tags, watch the VIDEO
How Vehicle Gate Access Control Systems Work
The reader checks the identification number against a database of authorized vehicles and, if the vehicle is authorized, grants access. The system can be configured to trigger an alarm or alert if an unauthorized vehicle attempts to enter the restricted area.

The benefits of using RFID UHF technology for Vehicle Access Control Systems include:
- High read range: RFID UHF technology allows for a read range of up to 72 ft / 22 meters, making it suitable for high-speed vehicle access control applications.
- Faster data transfer rates: Compared to other RFID technologies, RFID UHF technology has a faster data transfer rate, allowing for quicker identification and processing of vehicles.
- Reduced manual intervention: RFID UHF technology automates the access control process, reducing the need for manual intervention and improving the overall efficiency of the system.
- Improved security: RFID UHF technology provides a high level of security by ensuring that only authorized vehicles are granted access to the restricted area.
In summary, RFID UHF-based vehicle access control systems provide an efficient, automated, and secure way of managing vehicle access to restricted areas.
When Choosing A Vehicle Control System
When choosing a Vehicle Access Control System, there are several factors to consider to ensure that the system meets your specific needs and requirements. Some of the key factors to pay attention to include:
- Type of system: There are several types of Vehicle Access Control Systems, including barrier systems, RFID systems, license plate recognition systems, key card systems, and biometric systems. Consider the type of system that is best suited for your application, based on the level of security required, the type of vehicles accessing the area, and the volume of traffic
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the system, especially if you expect the number of vehicles and users to increase over time. Ensure that the system can be easily expanded to accommodate future growth without significant additional costs.
- Integration: Consider the integration capabilities of the system, especially if you need to integrate it with other security or access control systems. Ensure that the system can integrate with your existing infrastructure, or that it can be easily modified to integrate with new systems as needed.
- Reliability: Consider the reliability of the system, especially if it is critical to your operation. Ensure that the system is designed and manufactured to high-quality standards, and that it has a track record of reliable performance.
- User-friendliness: Consider the user-friendliness of the system, especially if it is used by a variety of people, such as employees, visitors, or tenants. Ensure that the system is easy to use and understand, with clear instructions and user-friendly interfaces.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the system, including the initial purchase price, installation costs, and ongoing maintenance and support costs. Ensure that the system provides value for money and fits within your budget.
Overall, it is important to carefully evaluate your specific requirements and consider all of these factors when choosing a vehicle access control system, to ensure that you select the right system for your needs.
Use of Long-Range Wireless Technologies In Vehicle Gate Access Control Systems

Parking access control systems manufactured by FRESH USA have been tested for many years of use around the world and work perfectly in all weather conditions. vehicle access control systems developed by Fresh USA uses only contactless technologies such as Wi-Fi, 4G / LTE and RFID UHF long range distance with a frequency of 860MHz – 960MHz. You can integrate the parking management software with other third-party software or your ERP system using a SQL database or deploy a Web-service.
Any RFID parking system, from Fresh USA is Your reliable choice.
The main advantage of a Vehicle Access Control System with RFID UHF technology is the high read range, which allows for efficient and convenient access control of vehicles without the need for physical contact or line-of-sight communication.
Compared to other access control systems, such as barcodes or magnetic stripe cards, RFID UHF systems offer the following advantages:
Long read range: RFID UHF systems can read tags from a distance of up to 72 ft / 22 meters, allowing for fast and efficient vehicle access control, even at high speeds.
High accuracy: RFID systems have a high accuracy rate, ensuring that only authorized vehicles are granted access to the restricted area.
No physical contact: RFID systems do not require physical contact between the reader and the tag, making them less prone to wear and tear, and requiring less maintenance.
High throughput: RFID UHF systems can process a large number of vehicles in a short period, reducing the waiting time for vehicles entering or exiting the restricted area.
Robustness: RFID systems are robust and can operate in harsh environmental conditions, such as rain, snow, and extreme temperatures.
Overall, the main advantage of a Vehicle Access Control System with RFID UHF technology is its ability to provide fast, efficient, and accurate access control of vehicles without the need for physical contact or line-of-sight communication, making it a convenient and reliable solution for managing vehicle access to restricted areas.
Chicago, Vehicle Access Control Systems
Vehicle Access Control Systems: Enhancing Security and Streamlining Access
1. Introduction to Vehicle Access Control Systems
1.1 Definition and Overview
Vehicle access control systems are sophisticated security solutions designed to regulate the entry and exit of vehicles within a specific area—be it a corporate campus, gated community, industrial site, or high-security government facility. Think of these systems as the traffic lights to your kingdom, ensuring that only those who have the right “green light” can pass through. By leveraging cutting-edge technology, we can safeguard property, protect personnel, and maintain a smooth flow of vehicles.
1.2 Importance of Regulating Vehicle Access
Why all the fuss about regulating vehicle access? It’s simple: security and efficiency. Unauthorized vehicles can pose a threat, leading to potential theft, vandalism, or worse. Meanwhile, bottlenecks during rush hour can be a nightmare without proper control in place. Vehicle access control systems address both concerns, creating a safer environment while keeping traffic organized and moving.
Free Online Estimate of Vehicle Access Control Systems
We provide Lifetime Software License. No Subscriptions, No Monthly Fees!
Parking Management Software Free Download
2. Historical Evolution of Vehicle Access Control
2.1 Early Security Measures
Before advanced electronics came into play, controlling vehicle access was a very manual process. Guards stood at gates, noting down license plates or simply relying on visual checks. Think of medieval castle gates with a drawbridge—except instead of knights, we had security guards armed with a clipboard.
2.2 The Rise of Electronic Systems
As technology progressed, so did our ability to automate. Magnetic stripe cards, simple keypads, and remotely operated gates began to pop up. These early electronic systems were a leap forward, but they still required a lot of human oversight and maintenance.
2.3 Modern-Day Innovations
Enter the era of advanced sensors, high-resolution cameras, and cloud-based management. Modern systems are not only more secure but also smarter, leveraging data analytics and real-time monitoring to offer insights that were unimaginable a few decades ago.
3. Core Components of Vehicle Access Control
3.1 Identification Methods
Any robust vehicle access control system starts with proper identification. The system needs to know who (or which vehicle) is trying to gain entry. Identification can be done through RFID tags, license plates, biometric data, key cards, or even mobile apps.
3.2 Physical Barriers and Gates
Once identification is confirmed, physical barriers like gates, bollards, or road blockers come into play. These act as the tangible “lock” that either grants or denies entry. They’re often automated, lifting or lowering based on the system’s decision.
3.3 Centralized Management and Monitoring
Central control hubs or software dashboards oversee all activities, log events, and allow administrators to manage permissions in real time. This centralized aspect ensures that security personnel don’t have to scramble between multiple checkpoints, making the entire operation more efficient.
Free Online Estimate of Vehicle Access Control Systems
We provide Lifetime Software License. No Subscriptions, No Monthly Fees!
Parking Management Software Free Download
4. Types of Vehicle Access Control Technologies
4.1 RFID (Radio Frequency Identification)
RFID relies on tags placed on or inside vehicles. As the vehicle approaches a reader, data is exchanged wirelessly, granting or denying access within milliseconds. This is particularly handy in busy parking lots, where throughput is a priority.
4.2 License Plate Recognition (LPR) Systems
LPR systems use cameras and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software to read plates and match them against a database. This is like having a photographic memory for license plates—never forgetting who’s allowed and who’s not.
4.3 Biometric Access Control
Biometric systems identify the driver by unique physical traits such as fingerprints, facial features, or even retinal scans. This method adds another layer of security, ensuring it’s not just the correct vehicle but also the correct person.
4.4 Keypad and Key Card Systems
For smaller facilities or situations where cost is a bigger factor, traditional keypads and key cards still do the job. While they may not boast the sleekness of RFID or biometrics, they’re familiar and relatively simple to operate.
5. Key Benefits of Implementing Vehicle Access Control
5.1 Improved Security and Safety
By identifying vehicles in advance and controlling physical barriers, the risk of unauthorized intrusion drastically decreases. This is especially beneficial for critical infrastructures like government buildings or data centers, where the margin for error is zero.
5.2 Streamlined Traffic Flow
Automated systems reduce the need for manual checks, thereby cutting down waiting times. Think of it as moving from a toll booth with a line of cars to an electronic pass lane—nobody likes to idle in a queue.
5.3 Cost Savings and Efficiency
While initial setup costs can be substantial, the long-term operational savings—fewer guards, reduced human error, and better asset protection—often justify the expense. Plus, the data collected can optimize everything from staffing levels to maintenance schedules.
5.4 Enhanced Data Collection and Analytics
Modern systems log entry and exit times, vehicle details, and potential security flags. This data can be analyzed to optimize traffic flow, identify patterns, and detect suspicious activities. Information is power, and here, it’s used to create a safer environment.
6. RFID Technology in Detail
6.1 How RFID Tags and Readers Work
RFID tags contain a small chip and antenna. When they enter the electromagnetic field of an RFID reader, they transmit stored data—like a unique ID code. The reader checks this code against a database, and if there’s a match, gates open almost instantly.
6.2 Advantages and Limitations of RFID
Advantages include speed, convenience, and relatively low maintenance. However, RFID can be vulnerable to interference from certain materials (like metal structures) and may require careful placement of readers to ensure consistent coverage. Still, for most applications, RFID strikes a great balance between speed and security.
7. License Plate Recognition (LPR) for High-Volume Areas
7.1 Camera Systems and OCR Software
LPR systems rely on cameras placed at strategic angles to capture license plates. Advanced OCR software then converts the image into alphanumeric data, verifying whether the vehicle is in the “allowed” list. It’s like a hawk-eyed guard with perfect memory.
7.2 Use Cases for LPR
Busy toll roads, airport parking, and major corporate campuses often rely on LPR to handle large volumes of vehicles. It’s contactless, efficient, and can even operate at high speeds, making it ideal for areas where congestion is a concern.
7.3 Minimizing Errors and False Positives
Occasional errors can happen due to poor lighting, dirty plates, or unusual fonts. High-resolution cameras, proper lighting, and robust software algorithms help minimize these hiccups, ensuring smooth operation day or night.
8. Biometric Vehicle Access Control
8.1 Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology can match real-time captures to a stored template of authorized drivers. This method is incredibly secure, though privacy concerns and high costs can be barriers to adoption.
8.2 Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprint sensors on vehicle dashboards or at access points verify the driver’s identity. While it’s reliable, environmental factors (like dirt, oils, or gloves) can sometimes affect accuracy.
8.3 Implementing Biometric Solutions Securely
Biometric data is sensitive, so encryption and strict data handling policies are crucial. Any breach could lead to severe privacy violations, making robust security measures a must.
9. Barrier and Gate Systems
9.1 Bollards, Gates, and Automated Barriers
Barrier systems physically prevent vehicles from passing until authorized. Bollards can rise out of the ground, gates can pivot or slide, and road blockers can impede heavier vehicles. Each is tailored to a different threat level, from mild deterrence to truck-stopping power.
9.2 Best Practices for Installation
When installing barriers, consider lane width, vehicle height, and space for drivers to maneuver. Also, ensure the system is fail-safe in case of power outages—nobody wants to be stuck on either side of a jammed gate.
9.3 Maintenance and Longevity
Regular checks for mechanical wear and tear, alignment, and software updates keep these systems at peak performance. A neglected barrier is an invitation for trouble.
10. Integration with Smart Technologies
10.1 IoT and Cloud-Based Platforms
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects multiple devices—cameras, sensors, readers—into a single, cohesive system. Cloud-based dashboards allow security teams to monitor gates, check logs, and even grant remote access, all from a central location.
10.2 Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Immediate notifications can be sent to security personnel if someone tries to force a gate or if an unauthorized vehicle attempts access. This proactive approach lets teams respond quickly, preventing potential breaches.
10.3 Scalability and Future-Proofing
Today’s systems can adapt to tomorrow’s challenges. As your facility grows, you can add more readers, cameras, or gates without overhauling the entire architecture. This modular approach ensures you’re not locked into a one-size-fits-all solution.
11. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
11.1 Technical Glitches
From malfunctions in hardware to network disruptions, technology isn’t infallible. Keep spare parts, maintain redundancy (like backup power sources), and schedule regular updates to minimize downtime.
11.2 User Adoption and Training
Fancy systems are useless if nobody knows how to use them. Ensure staff and residents (if it’s a residential area) understand how to operate tags, cards, or apps. Clear signage and instructions go a long way toward user compliance.
11.3 Privacy and Data Protection
Storing vehicle logs and biometric data raises privacy concerns. Encrypt stored data, use secure networks, and follow local regulations (like GDPR in Europe) to protect user rights and maintain trust.
12. Selecting the Right Vehicle Access Control System
12.1 Assessing Security Needs
Are you dealing with a high-risk environment, like a research lab with sensitive data, or do you just want to ensure your corporate parking lot stays private? Align your system choice with the threat level.
12.2 Budget Considerations
Costs can vary widely, from simple keypad entries to advanced biometric setups. Factor in not just the upfront cost but also ongoing expenses like maintenance, software licensing, and potential upgrades.
12.3 Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
It’s like trying to fit a puzzle piece into a nearly complete picture—if the system doesn’t integrate seamlessly, you’ll end up with gaps. Ensure your new system can talk to existing security cameras, alarms, or other relevant setups.
12.4 Vendor Evaluation and Support
A shiny demo is great, but will the vendor provide timely support when the system goes haywire at 3 AM? Check service agreements, reviews, and reliability to avoid nasty surprises down the road.
Free Online Estimate of Vehicle Access Control Systems
We provide Lifetime Software License. No Subscriptions, No Monthly Fees!
Parking Management Software Free Download
13. Case Studies: Practical Applications
13.1 Commercial Complexes
Large office parks often use RFID to handle hundreds of employees’ vehicles daily, integrating it with HR databases so employees’ permissions get updated instantly. This keeps gates moving smoothly without compromising security.
13.2 Residential Communities
Gated neighborhoods can benefit from LPR or card access systems, ensuring only residents and registered guests enter. Think of it as a friendly neighborhood watch, but automated.
13.3 Industrial and Government Facilities
High-security sites may combine multiple technologies—RFID for fast recognition, biometrics for driver ID, and heavy-duty barriers to deter forced entry. It’s a multi-layered defense strategy that leaves little room for breaches.
14. Future Trends in Vehicle Access Control
14.1 Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
AI can identify unusual patterns—like a vehicle that appears at odd hours or repeatedly attempts access—and flag them for review. It’s proactive security, anticipating issues before they become crises.
14.2 Touchless and Contactless Solutions
In a world that values hygiene and convenience, touchless solutions (like facial recognition or automated gate lifting) are on the rise. No more fumbling for passes or tapping keypads.
14.3 Integration with Smart Cities
Picture a future where city-wide networks coordinate traffic lights, parking, and public safety measures. Vehicle access control systems will plug into these networks, contributing to fluid city traffic management and robust overall security.
15. Conclusion
Vehicle access control systems are more than just gates and cameras; they represent a holistic approach to security and logistics. Whether you choose RFID for high-traffic commercial complexes or a biometric system for top-secret government facilities, the core goal remains the same: protecting assets, streamlining entry, and ensuring peace of mind.
As we move toward an increasingly interconnected future, these systems will continue to evolve—embracing AI, cloud computing, and IoT to become even more efficient, intuitive, and secure. In a world where threats are unpredictable and time is precious, implementing the right vehicle access control system can mean the difference between chaos and calm.
FAQs
- Which Access Control System Offers the Highest Security?
Biometric systems often offer the highest level of security because they verify the driver’s unique physical attributes. However, a multi-layered approach combining different technologies can be even more secure. - How Much Does a Typical Vehicle Access Control System Cost?
Costs vary widely based on the technology and complexity. A basic keypad system may cost a few hundred dollars, while high-end biometric or multi-layer solutions can run into tens of thousands. - Can I Integrate an Old Barrier Gate with Modern Technology?
In most cases, yes. Many modern systems are designed with backward compatibility in mind. However, the older the barrier gate, the more likely you’ll need some additional hardware or retrofitting. - What Are the Main Challenges When Using Biometric Access?
High cost, privacy concerns, and environmental factors (like weather or dirt) affecting the sensors are common challenges. Proper implementation and maintenance can mitigate these issues. - Is License Plate Recognition Reliable in Poor Weather Conditions?
Advanced LPR systems use high-resolution cameras and infrared lighting, which can handle rain or fog reasonably well. However, extremely adverse conditions might reduce accuracy slightly.