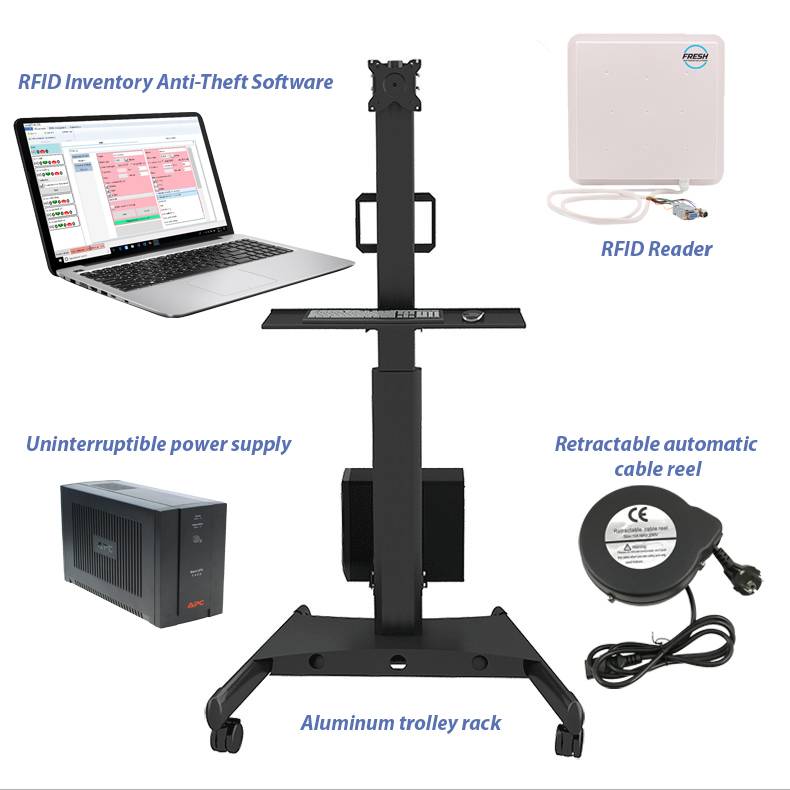
RFID Inventory Management System: The Ultimate Guide to Streamlining Your Operations
Introduction to RFID Inventory Management
In today’s fast-paced business world, managing inventory efficiently is more crucial than ever. The days of manually counting stock are long gone, thanks to technology. But what if we told you there’s a way to make inventory management even more seamless and accurate? That’s where RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, comes into play.
RFID technology is revolutionizing the way businesses track their inventory. From reducing errors to offering real-time tracking, RFID systems are becoming a game-changer in various industries. But how does it work, and is it right for your business? Let’s dive in.
Buy Inventory Reader
Prices and Buy RFID Systems
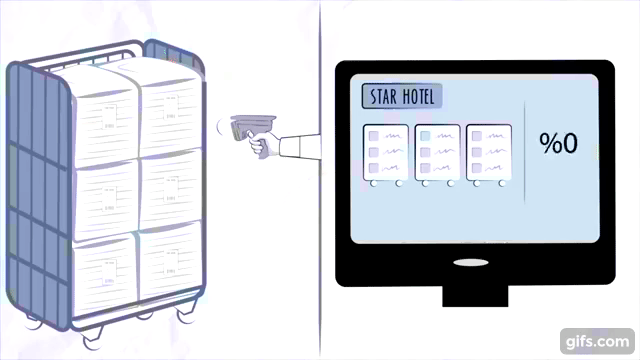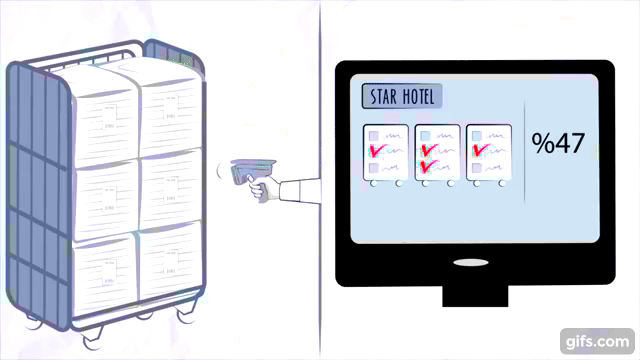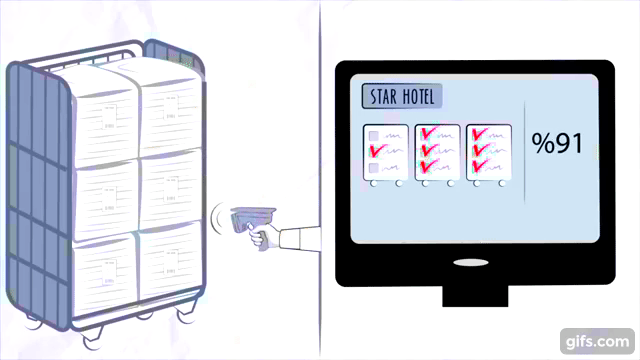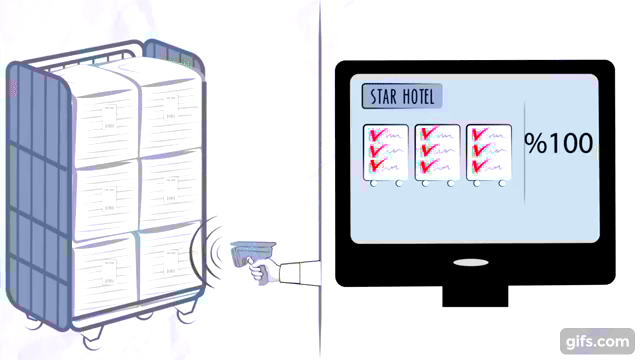
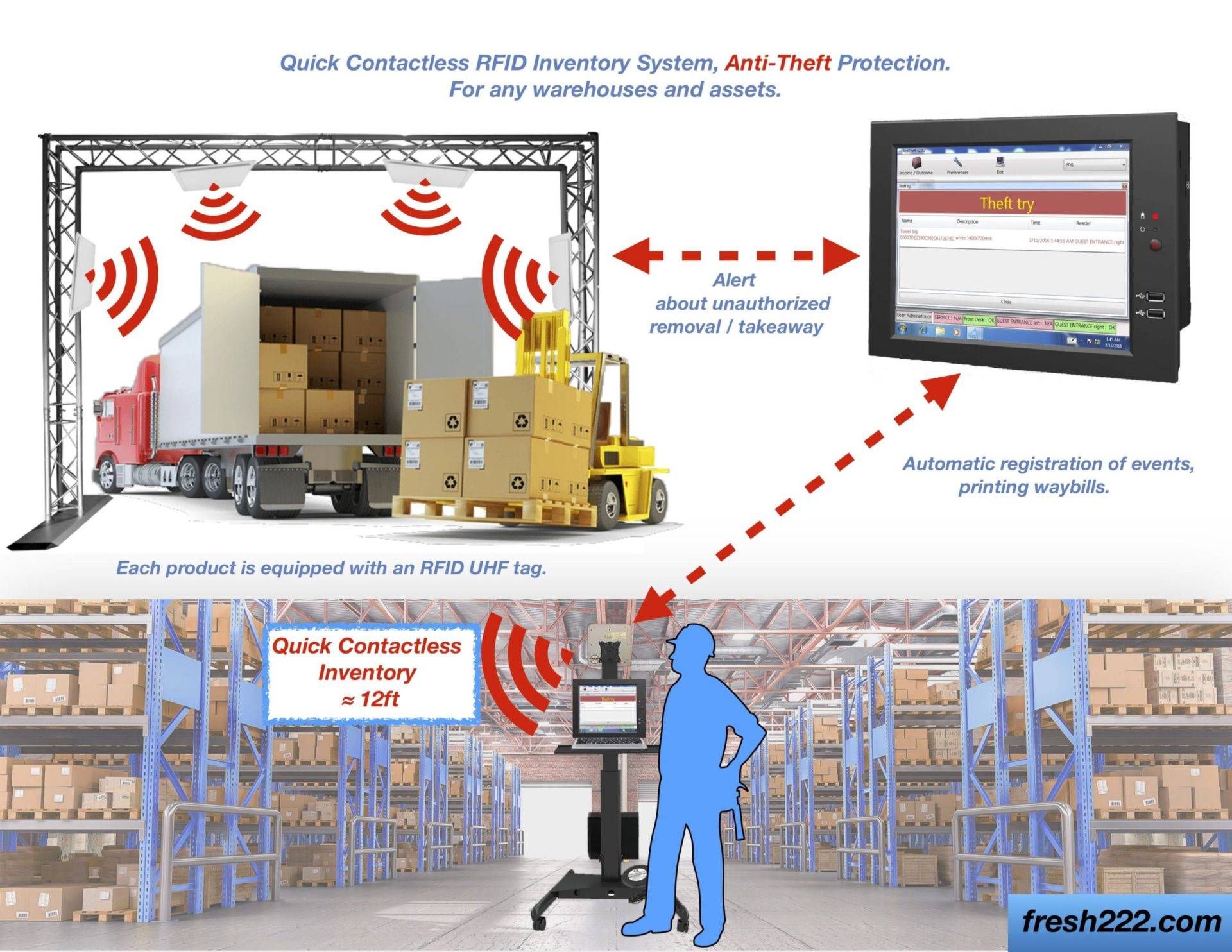
How RFID Technology Works
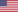
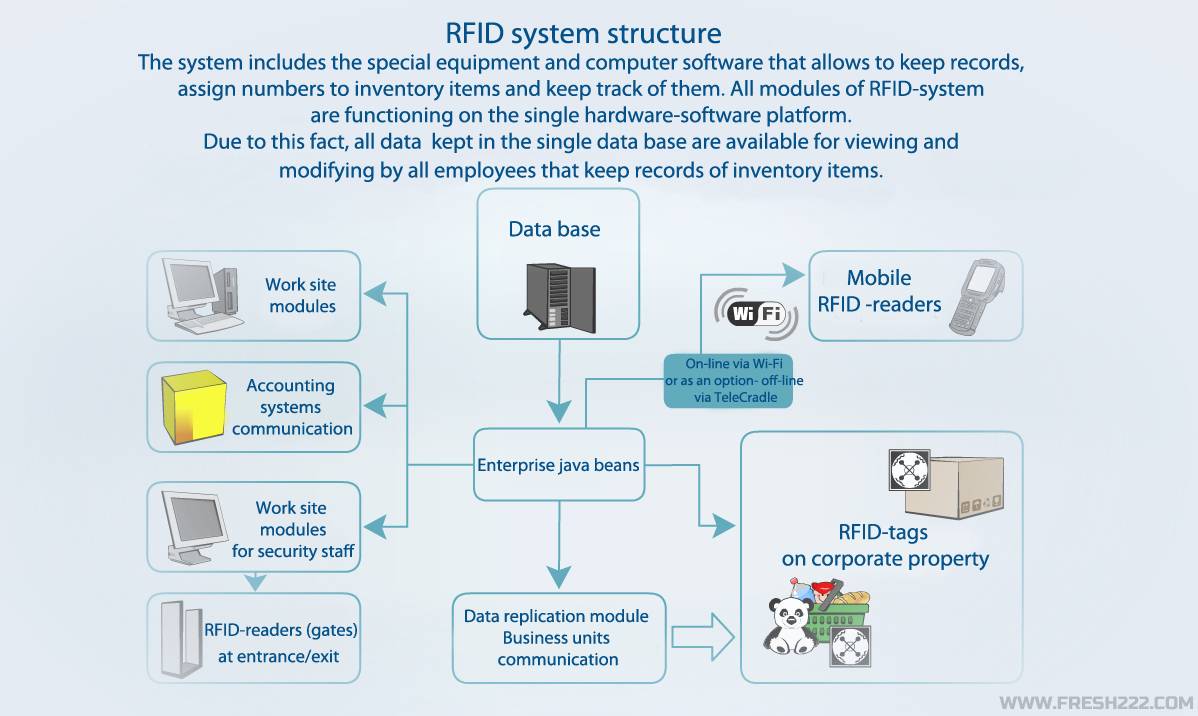
Components of an RFID System
An RFID inventory management system consists of three key components:
- RFID Tags: These are small devices attached to the inventory items. They contain microchips that store data about the item.
- RFID Readers: Devices that emit radio waves to read the information stored in RFID tags.
- Backend Database: A centralized system where all the collected data is stored, processed, and analyzed.
RFID Tags: Passive vs. Active
There are two types of RFID tags:
- Passive Tags: These tags do not have their own power source. They rely on the reader’s signal to power up and transmit data. They are more cost-effective but have a shorter range.
- Active Tags: These have their own battery and can transmit data over longer distances. They are more expensive but offer more reliability and functionality.
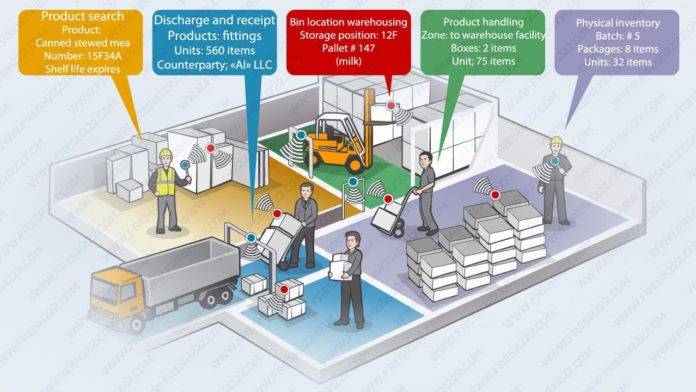
RFID Readers and Antennas
RFID readers can be handheld or fixed. They use antennas to send radio waves to communicate with RFID tags. The choice of reader and antenna depends on the application and the environment in which they are used.
Write A Request
Key Benefits of RFID in Inventory Management
Enhanced Inventory Accuracy
One of the most significant advantages of RFID is its ability to provide near-perfect inventory accuracy. Unlike barcodes, which require manual scanning, RFID tags are read automatically, reducing human errors and improving inventory tracking accuracy by up to 99.9%.
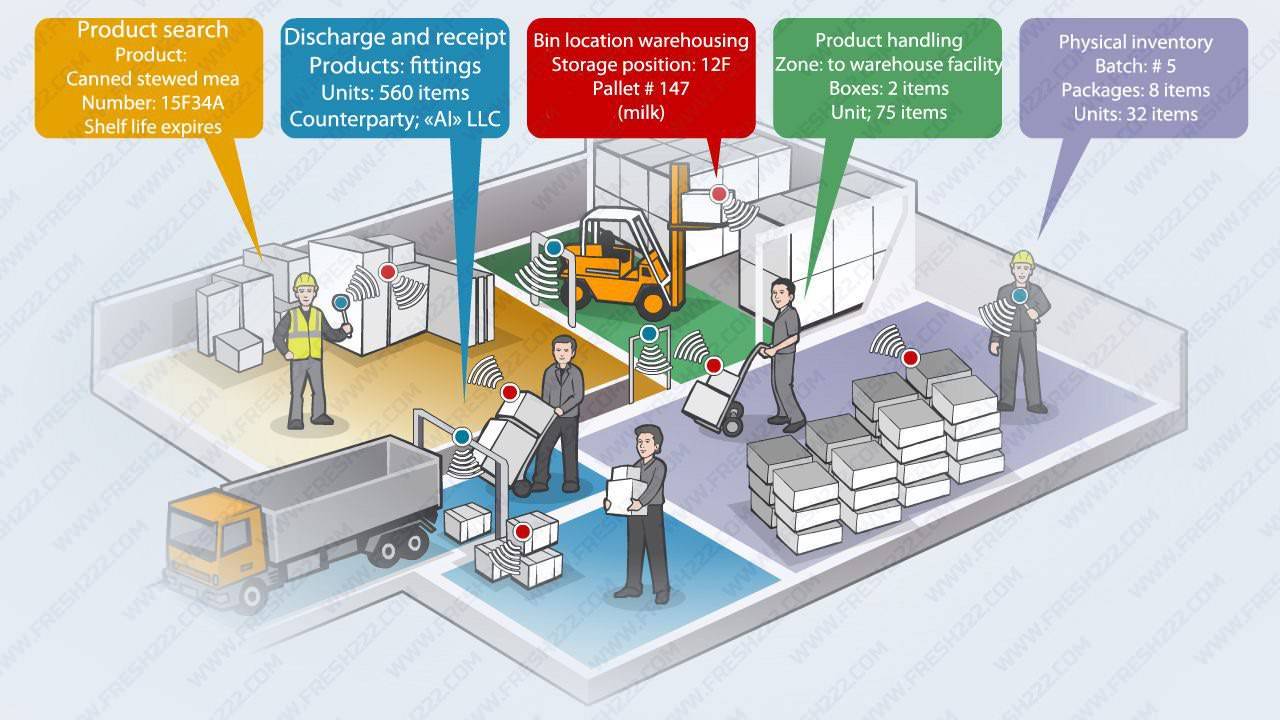
Real-Time Visibility and Tracking
RFID provides real-time updates on inventory status. You know exactly where every item is at any given moment, whether it’s in transit, on a shelf, or in the warehouse. This real-time tracking reduces stockouts and overstock situations.
Reduced Labor Costs
With RFID, the need for manual scanning and inventory checks is minimized. This automation reduces labor costs, allowing staff to focus on more value-added activities rather than spending hours on inventory management tasks.
Improved Supply Chain Efficiency
RFID enables smoother supply chain operations by providing accurate data about stock levels and movement. This accuracy ensures timely replenishments, reducing the likelihood of delays and disruptions.
Buy Inventory Reader
Prices and Buy RFID Systems
Challenges of Implementing RFID Technology
Initial Setup Costs
Implementing RFID technology involves significant initial costs, including purchasing RFID tags, readers, and necessary infrastructure. However, these costs can often be recouped through long-term savings in labor and efficiency.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating RFID with existing inventory management and enterprise systems can be complex and require significant IT resources. It’s crucial to choose a system that integrates seamlessly with your current software.
Privacy and Security Concerns
RFID technology can raise privacy concerns, especially in consumer environments where tags might inadvertently capture personal data. Businesses must implement robust security measures to protect data and ensure compliance with regulations.
Write A Request
How to Implement RFID in Your Business
Step-by-Step Implementation Plan
- Assess Your Needs: Determine what you want to achieve with RFID – improved accuracy, reduced costs, better customer service, etc.
- Choose the Right System: Select an RFID solution that fits your business requirements, considering factors like range, cost, and compatibility.
- Plan the Infrastructure: Set up the necessary hardware and software, including RFID readers, antennas, and backend systems.
- Training and Support: Train your staff on how to use the new system effectively.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review the performance of your RFID system and make necessary adjustments.
RFID vs. Barcode: Which is Better for Inventory Management?
Pros and Cons of RFID
- Pros: Faster scanning, no line-of-sight needed, real-time tracking, improved accuracy.
- Cons: Higher initial costs, potential privacy issues.
Pros and Cons of Barcodes
- Pros: Lower cost, widely adopted, simple technology.
- Cons: Requires manual scanning, prone to human error, limited data storage.
Comparing Use Cases
RFID is ideal for businesses that need real-time tracking and manage a large number of high-value items, while barcodes may suffice for smaller businesses with less complex inventory needs.
Industries Benefiting from RFID Inventory Management
- Retail: Improves stock accuracy and reduces shrinkage.
- Healthcare: Enhances tracking of medical supplies and equipment.
- Manufacturing: Streamlines production processes and reduces downtime.
- Logistics and Warehousing: Optimizes storage and distribution.
Buy Inventory Reader
Prices and Buy RFID Systems
Future Trends in RFID Technology
IoT Integration
RFID is increasingly being integrated with the Internet of Things (IoT) to enable smarter inventory management systems that provide even more data insights.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being used to analyze RFID data, predicting trends and automating decision-making processes.
Advancements in RFID Tags
New developments in RFID tags, such as printable and biodegradable tags, are making the technology more versatile and environmentally friendly.
Best Practices for RFID Inventory Management
- Conduct regular audits to ensure RFID tags are functioning correctly.
- Implement strong security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Continuously evaluate and improve your RFID processes.
Common Misconceptions About RFID Technology
- Myth: RFID is Too Expensive – While the initial costs may be high, the long-term savings in labor and accuracy make it a worthwhile investment.
- Myth: RFID Replaces Human Jobs – RFID technology complements human work by automating repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic roles.
- Myth: RFID is Difficult to Implement – With the right planning and support, RFID implementation can be straightforward.
Case Studies: Successful RFID Implementations
- Retail Chain Success: A global retail chain reduced inventory inaccuracies by 85% and increased sales by 5% after implementing RFID.
- Healthcare Efficiency: A hospital cut down its inventory costs by 20% by using RFID to track medical supplies.
- Warehouse Optimization: A large warehouse reduced order picking errors by 90% after switching to an RFID-based system.
Write A Request
Cost-Benefit Analysis of RFID Implementation
To determine the ROI, consider both the initial costs and the long-term savings. While RFID systems may require a significant upfront investment, they often pay for themselves within a few years through reduced labor costs, improved accuracy, and greater efficiency.
RFID Inventory Management and Sustainability
RFID helps reduce waste by ensuring accurate inventory tracking, which minimizes overproduction and stockouts. It also supports green initiatives by reducing the carbon footprint associated with manual inventory management.
Conclusion: Is RFID Right for Your Business?
RFID technology offers numerous benefits, from improving inventory accuracy to reducing labor costs. However, it also comes with its challenges, such as initial setup costs and integration complexities. By carefully considering these factors and planning accordingly, businesses can decide if RFID is the right choice for them.
FAQs
- What is an RFID inventory management system?
An RFID inventory management system uses radio frequency identification technology to track and manage inventory automatically, providing real-time data and improving accuracy.
- How much does it cost to implement RFID technology?
The cost varies depending on the size of the implementation, the type of RFID tags and readers used, and the complexity of the integration. However, most businesses find that the long-term benefits outweigh the initial costs.
- Can RFID work with existing inventory management systems?
Yes, RFID can be integrated with most existing inventory management systems, but it may require some adjustments or additional software.
- What types of businesses benefit the most from RFID?
Businesses in retail, healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics benefit significantly from RFID due to the need for real-time inventory tracking and reduced errors.
- What are the future trends in RFID technology?
Future trends include IoT integration, advancements in RFID tags, and the use of AI and machine learning to analyze RFID data.