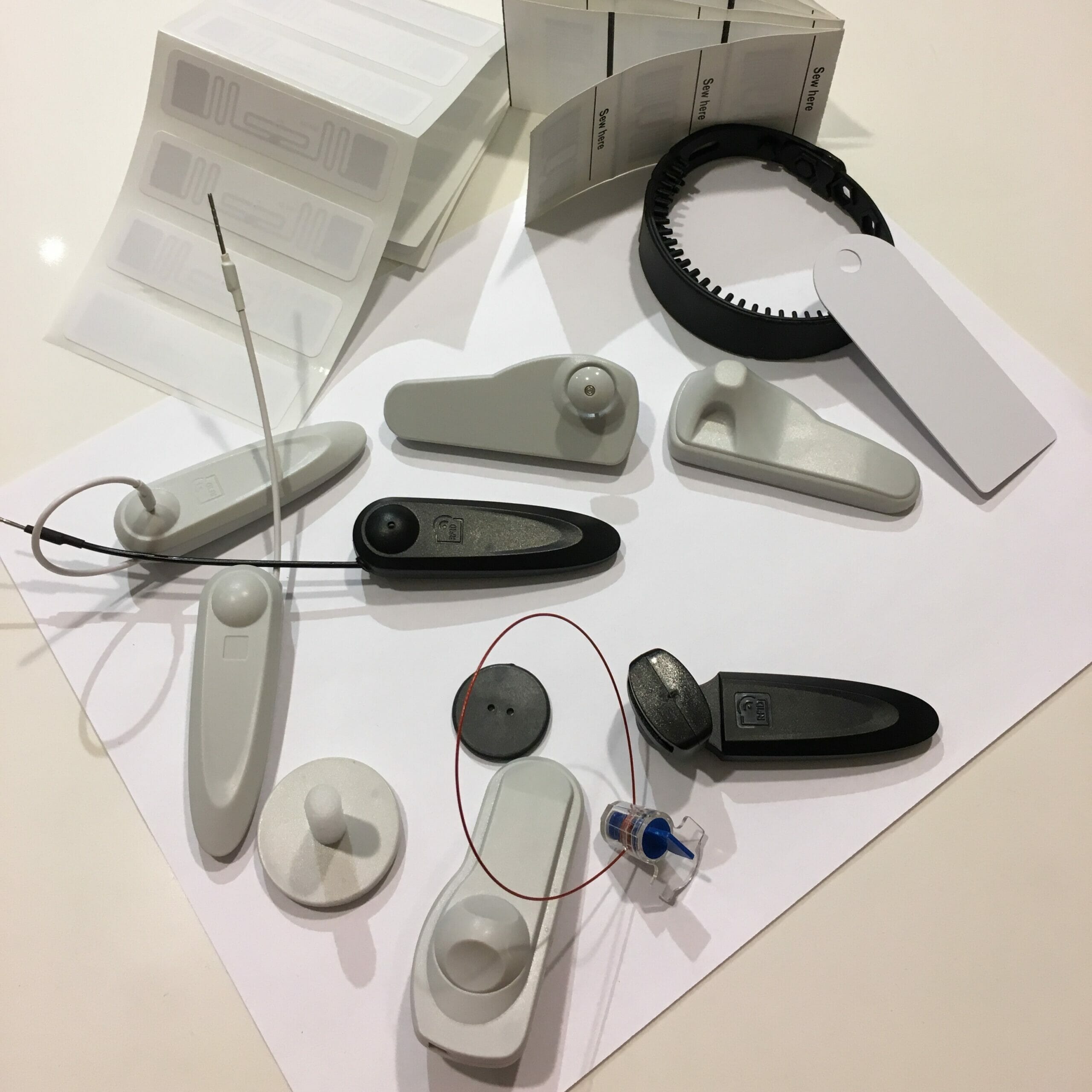
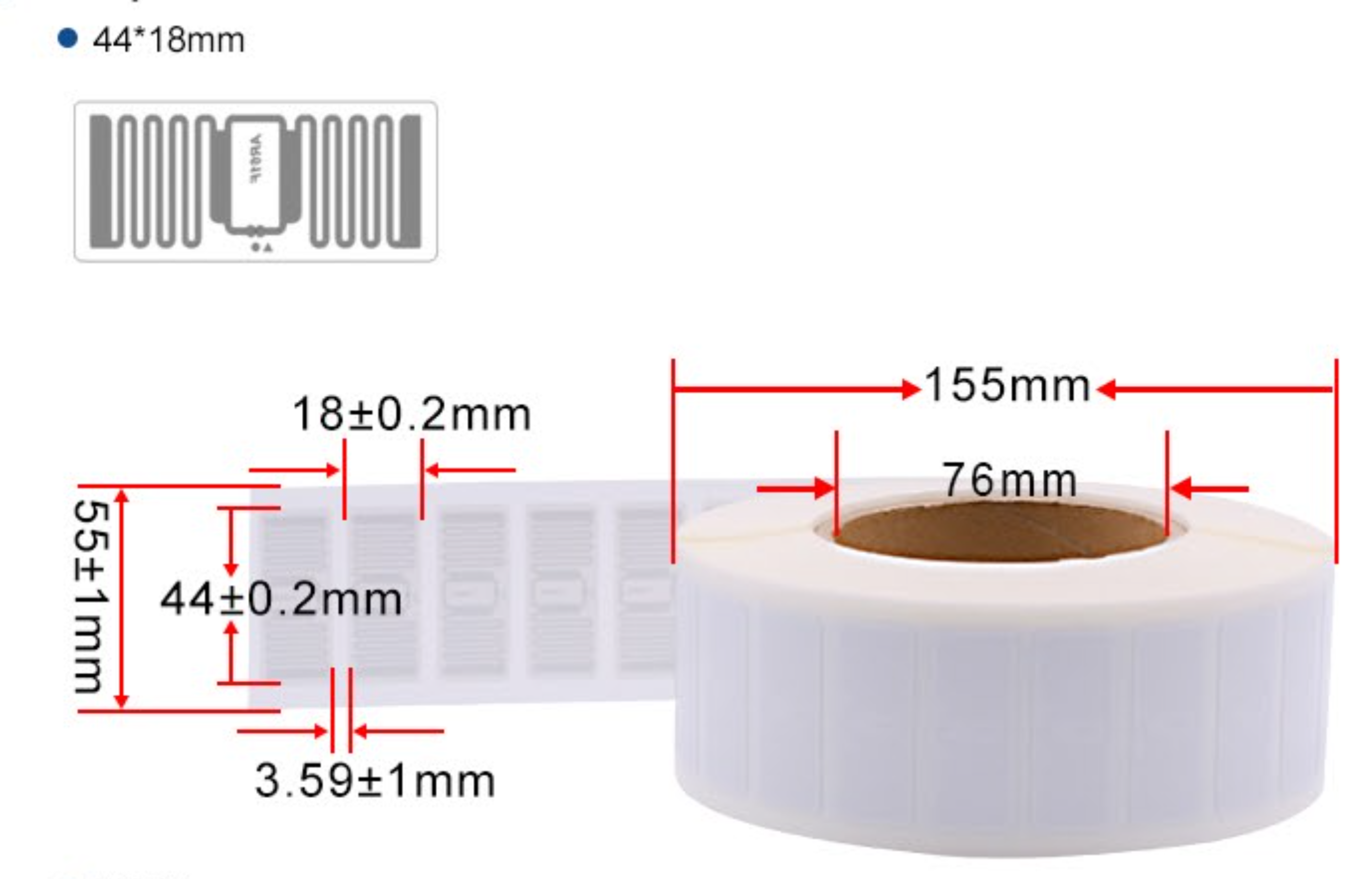
RFID UHF tags (Radio Frequency Identification Ultra-High Frequency tags) are electronic devices that use radio waves to remotely identify and track objects. They are a type of RFID tag that operates at higher frequency ranges, typically between 860 MHz and 960 MHz. UHF tags are widely used in various industries, including logistics, inventory management, supply chain, and asset tracking.
Introduction
There are no universal tags! At the beginning you should understand how to properly use various types of tags for different types of objects. Because different types of tags are designed for different goods, assets, objects. If you are not sure, contact a specialist for help. These tags consist of a microchip and an antenna, which are encased in a protective material. The microchip stores data or information related to the tagged object, while the antenna enables communication between the tag and an RFID reader. When an RFID reader emits radio waves, the UHF tag receives the energy from the waves, allowing it to power up and transmit its stored data back to the reader.
UHF tags offer several advantages over other types of RFID tags. They have a longer read range, meaning they can be read from a greater distance compared to lower frequency tags. This makes UHF tags ideal for applications where large numbers of tags need to be read simultaneously and quickly, such as in warehouses or retail environments. UHF tags also have faster data transfer rates, allowing for more efficient and rapid data exchange between the tag and the reader.


These tags come in different form factors and designs to suit various applications. They can be adhesive labels that can be attached to objects or integrated into product packaging. UHF tags can also be embedded or sewn into fabrics, making them suitable for tracking textiles, garments, or laundry items. Additionally, specialized UHF tags are designed for use with liquids, such as bottles or containers.
Correct Testing And Application Of RFID UHF Tags

Anti-Metal RFID UHF Tags
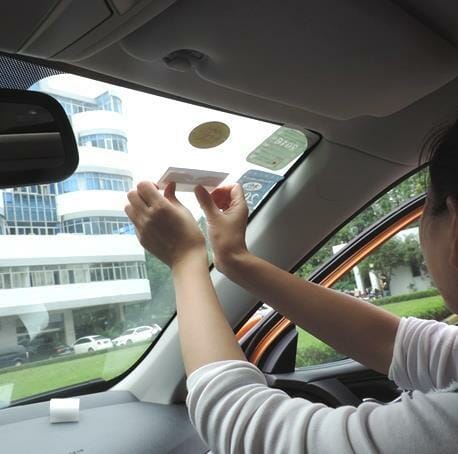
If the tag is anti-metal it should be pasted (glued) on the metal surface. Pasted on metal, but do not hold it in your hand!
The tag is so designed, it works better only on metal surfaces. Properly using and applying special Anti-metal RFID UHF tags is crucial to ensure their optimal performance in metal-rich environments. Depending on the tag’s design, use the appropriate adhesive or attachment method to affix the tag to the metal surface. Position the tag in an area on the metal surface that provides the best read performance. Avoid placing the tag too close to edges or corners of the metal, as these areas may experience increased interference. These tags are engineered to overcome the challenges posed by metal interference and ensure reliable read performance.
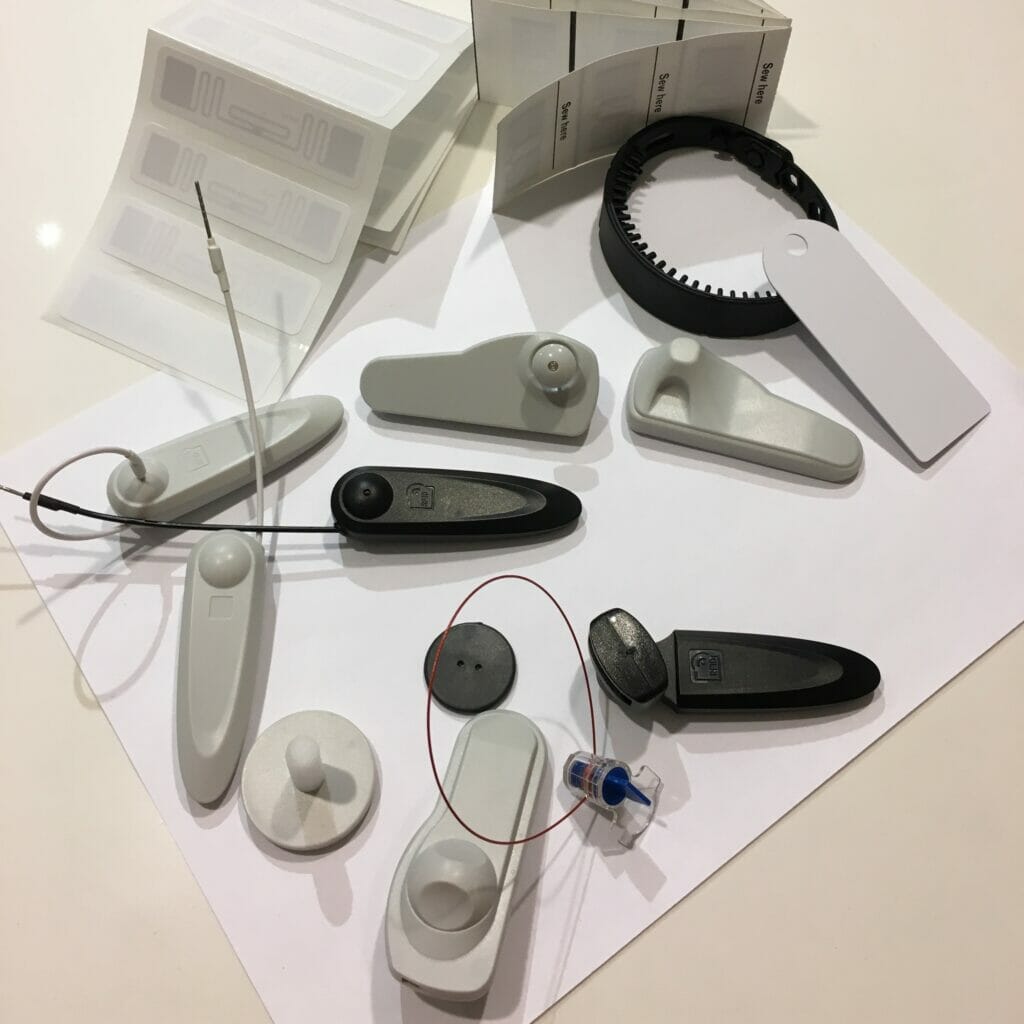 Regular RFID UHF Tags
Regular RFID UHF Tags
Properly using and applying regular RFID UHF tags ensures their effective functionality and accurate data capture. If you have the regular tags as stickers, hard tags, to stick it on a cardboard box, plastic and the like. It can not be glued to metal surfaces or used for liquid !!! You can not test tags in your hand !!! You have to test it as it should work REALLY. Choose tags suitable for your specific application and environment. Attach the RFID tag to the desired surface or fabric following the manufacturer’s instructions. Use the adhesive backing on the tag or any recommended attachment method provided. Consider the tag’s orientation and placement to ensure it can be easily detected by the RFID reader. Avoid placing the tag near metal objects or liquids that may interfere with its performance.
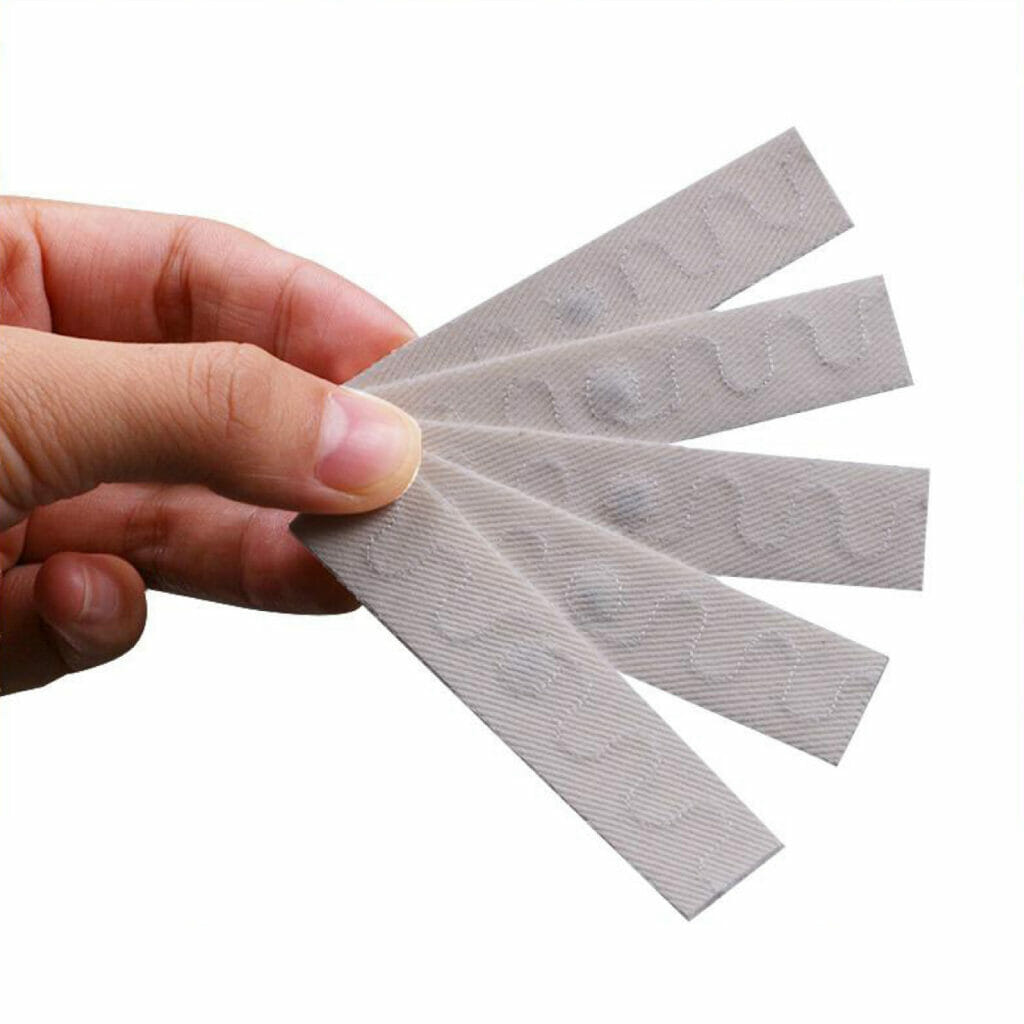

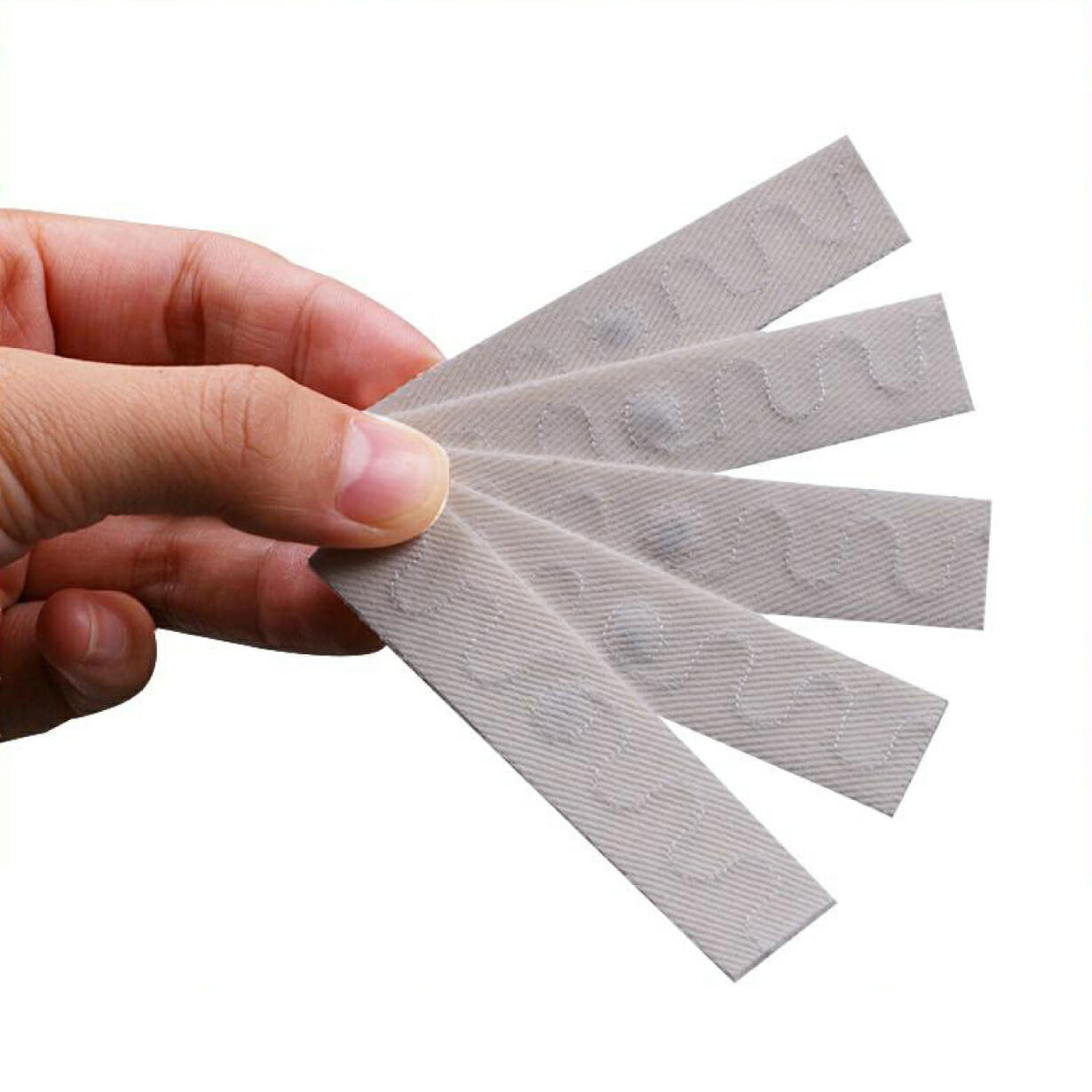
Laundry Washable Textile RFID UHF Tags
Properly using and applying laundry washable textile RFID UHF tags ensures their durability and effective tracking in textile-related applications. If you have laundry RFID tags, it’s best to sew them into the fabric! If tags for clothes, you should hang them on clothes. For sew-on tags, use a sewing machine or needle and thread to securely stitch the tag onto the fabric. These tags work well for the rental service for clothes, towels, robes, linen. For iron-on tags, follow the instructions provided to apply the tag using heat and pressure. Place the RFID tag in a position that allows for easy detection and readability while considering the textile item’s characteristics. Avoid placing the tag in areas that may cause discomfort or hinder the item’s functionality.

RFID UHF Tags For Liquids
Special RFID tags for bottles and water, tags used for liquids. When using special RFID UHF tags for liquids, such as water or oil, it is essential to follow proper guidelines to ensure their effective use and application. Remember, it is crucial to select RFID UHF tags specifically designed for liquids and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper use and application. Consider the orientation and placement of the tag to maximize its readability. Avoid positioning the tag near metal or other objects that may interfere with the radio frequency signals. By following these guidelines, you can effectively utilize these specialized tags for tracking and managing liquids, water, oil, or other similar substances in various industrial, manufacturing, or logistics applications.
Anti-Tamper RFID UHF Tags

These tags come with an additional security feature that protects against unauthorized removal or tampering. The unique aspect of these tags is that if they are removed in an unauthorized manner, unglued, or cut off, the embedded chip within the tag is self-destructed. This self-destruction renders the RFID tag and chip useless. When the tag is tampered with, it is no longer readable by an RFID reader, effectively becoming lost and out of the field of action. The software system connected to the RFID reader recognizes this and triggers an alarm signal to alert security or relevant personnel. The purpose of using these anti-tamper RFID UHF tags is to ensure the integrity and security of valuable items. By incorporating this self-destruct mechanism, attempts to remove or tamper with the tag are immediately detected and responded to, preventing unauthorized access or theft. Be careful, these tags are designed to work with a smart shelf solution and inventory management only. These tags will not work with a theft prevention system!
3D RFID UHF tags

A 3D RFID UHF tag is designed with three-dimensional (3D) capabilities. Unlike traditional RFID tags that are flat and operate in a two-dimensional plane, 3D RFID UHF tags have the ability to be read from multiple angles and orientations. These tags are used for various purposes across different industries due to their unique features and advantages. 3D RFID UHF tags can be attached to products or pallets, allowing for efficient tracking and management of inventory throughout the supply chain. They can be read from different angles and even through packaging, making them ideal for automated inventory systems. The ability to read the tags from various orientations improves the accuracy and reliability of asset tracking systems. 3D RFID UHF tags can be integrated into product packaging or labels. They enable quicker and more accurate checkouts at the point-of-sale, as multiple items can be scanned simultaneously, even if they are not perfectly aligned with the reader. 3D RFID UHF tags are useful in industrial environments for tracking work-in-progress items, managing components in assembly lines, and monitoring the movement of goods within manufacturing facilities. 3D RFID UHF tags offer improved reading capabilities from various angles, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including supply chain management, asset tracking, retail, healthcare, industrial processes, access control, and waste management. Their versatility and efficiency make them valuable tools for enhancing productivity and security in various industries.

There are no universal tags!
You must correctly check the tags using their actual application.
The smaller the tag – the smaller its reading range.
The reading range is achieved by installing a powerful antenna.
RFID UHF Tags & Memory Banks
RFID technology’s main properties are remote identify and track tags attached to objects and informations exchange. Today we will talk about the security measures we can use to protect the data within an UHF RFID passive transponder. This standard is the most used kind of radio frequency in logistic and industrial applications for its ability to read multiple tags at far distance. And also we will talk about the new chip standard …Today the UHF RFID transponders are Class 1 Gen2. This kind of tag was release of 15 years ago in order to create to unify tag and hardware manufacturers under one global standard for a better interoperability. The previous version named Class 1 Gen1 contained virtually no security features because at the time security measures were auxiliary in production. In the 2004 newly emerging issues forcing EPC global and ISO to respond with increased security measures on UHF tags in the Gen2 standard. The results were to provide the first layer of protection against hackers through serialized TID numbers and passwords.
EPC
The EPC (Electronic Product Code) memory bank is a specific area within an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tag’s memory where the EPC-related information is stored. The EPC is a unique identifier assigned to each RFID tag and is used to identify and track individual products or items in a supply chain or inventory management system. The EPC memory bank contains the EPC code, which is a numerical or alphanumeric value that uniquely identifies the tagged item. This code serves as a key piece of information for accurate and efficient tracking and identification of products.
TID numbers
These numbers were introduced for identifications purposes but in these years became widely used for the authentication, due to its uniqueness for each tag and uncounterfeiting skills. Each tag leaves the factory with a unique TID number and it is not modifiable by a normal user. Generally, to authenticate a tag that is suspected to be fake, the only way to check it is reading the EPC memory bank and the TID memory bank, if they doesn’t match, that RFID tag is counterfeit.
User memory
The user memory bank is a section within an RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tag’s memory that is available for storing custom or user-specific data. Unlike the EPC (Electronic Product Code) memory bank, which contains standardized information and is primarily used for identification purposes, the user memory bank offers flexibility for storing data specific to the user’s needs or application.n The user memory bank is typically used to store additional information that is not covered by the standardized EPC memory bank. It allows users to customize the RFID tag by storing data such as product specifications, customer-specific details, maintenance records, or any other relevant information specific to the application or business requirements.
The capacity of the user memory bank can vary depending on the specific tag model and manufacturer. Some RFID tags may provide a few bytes or kilobytes of user memory, while others may offer larger memory capacities, allowing for more extensive data storage.
Passwords
On Class 1 Gen2 tags are available two different password functionalities: the access password and the kill password. Both passwords are stored in factory on the reserved memory block and come pre-encoded with zeros, which do not function as an access or kill code.
Access password
The access password on UHF Gen2 tags must be modified in order to be used. Four lock states exist on each memory bank:
Unlocked
Perma-unlocked (can never be locked)
Locked
Perma-locked (can never be unlocked)
When a memory bank is locked, only the RFID reader that interrogates it first with the access code could read it. The access code can also prevent readers from reading the reserved memory bank if it is locked. It is important to note that a small piece of software is usually required in order for the reader to interrogate the RFID tag.
Kill password
This code is used for applications that require tags to change state/phase to indicate a specific event has occurred. In retail applications it is used because once an item is purchased the tag can be killed, making it permanently unreadable. Many producer in different markets, that track their products during the manufacturing and storage phase, kill them when leave the factory.
In summary, RFID UHF tags are electronic devices that utilize radio waves to remotely identify and track objects. They offer a longer read range, faster data transfer rates, and are used in a wide range of industries for applications such as inventory management, asset tracking, and supply chain optimization.